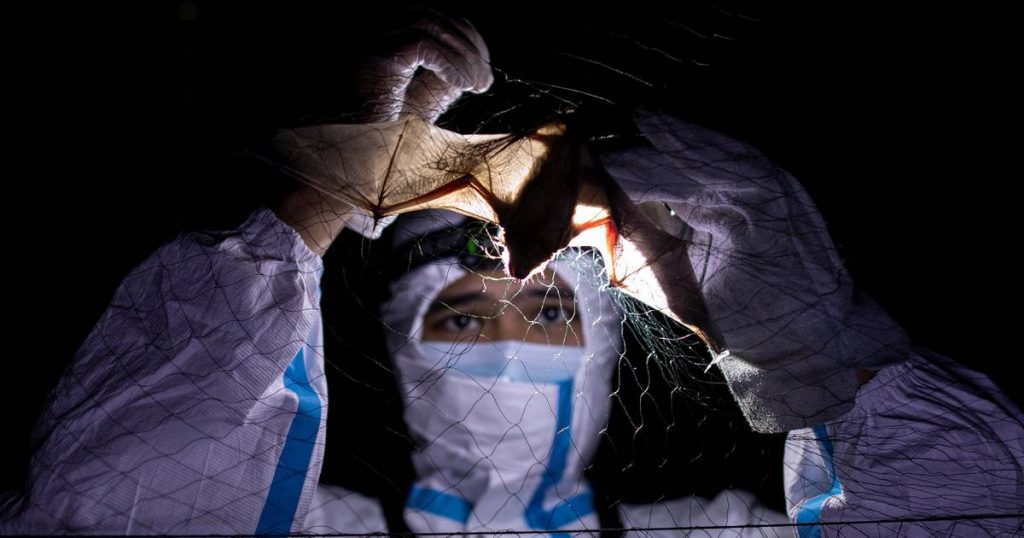
Scientists warn that climate change could cause up to 15,000 new transmissions of the virus between different animal species by 2070. After all, a runaway climate would drive bats to other regions.
It is no longer necessary to plot what this could mean, as the new coronavirus passed from bats to humans via a vector at the end of 2019.
With climate change, many animals will move to other habitats, along with parasites and pathogens. That would increase the risk of infectious diseases spreading from animals to humans in the next 50 years, according to the science journal Nature.
Danger
Species that have never come into contact with each other suddenly do so. The risk will be greater in densely populated areas, especially in tropical Africa and Southeast Asia.
The study examined how global changes in the future could create “hotspots” where viruses travel and diseases originate. She outlined how animals would move if the Earth’s temperature rose by 2 degrees by 2070 and their current habitats were no longer suitable for them.
Scientists have estimated that there will be at least 15,000 new transmissions of viruses between animal species, driven primarily by bats, which carry viruses that can easily be transmitted to humans.
Unlimited free access to Showbytes? And that can!
Sign in or create an account and never miss a thing from the stars.

“Total coffee specialist. Hardcore reader. Incurable music scholar. Web guru. Freelance troublemaker. Problem solver. Travel trailblazer.”






More Stories
GALA lacks a chapter on e-health
Weird beer can taste really good.
Planets contain much more water than previously thought