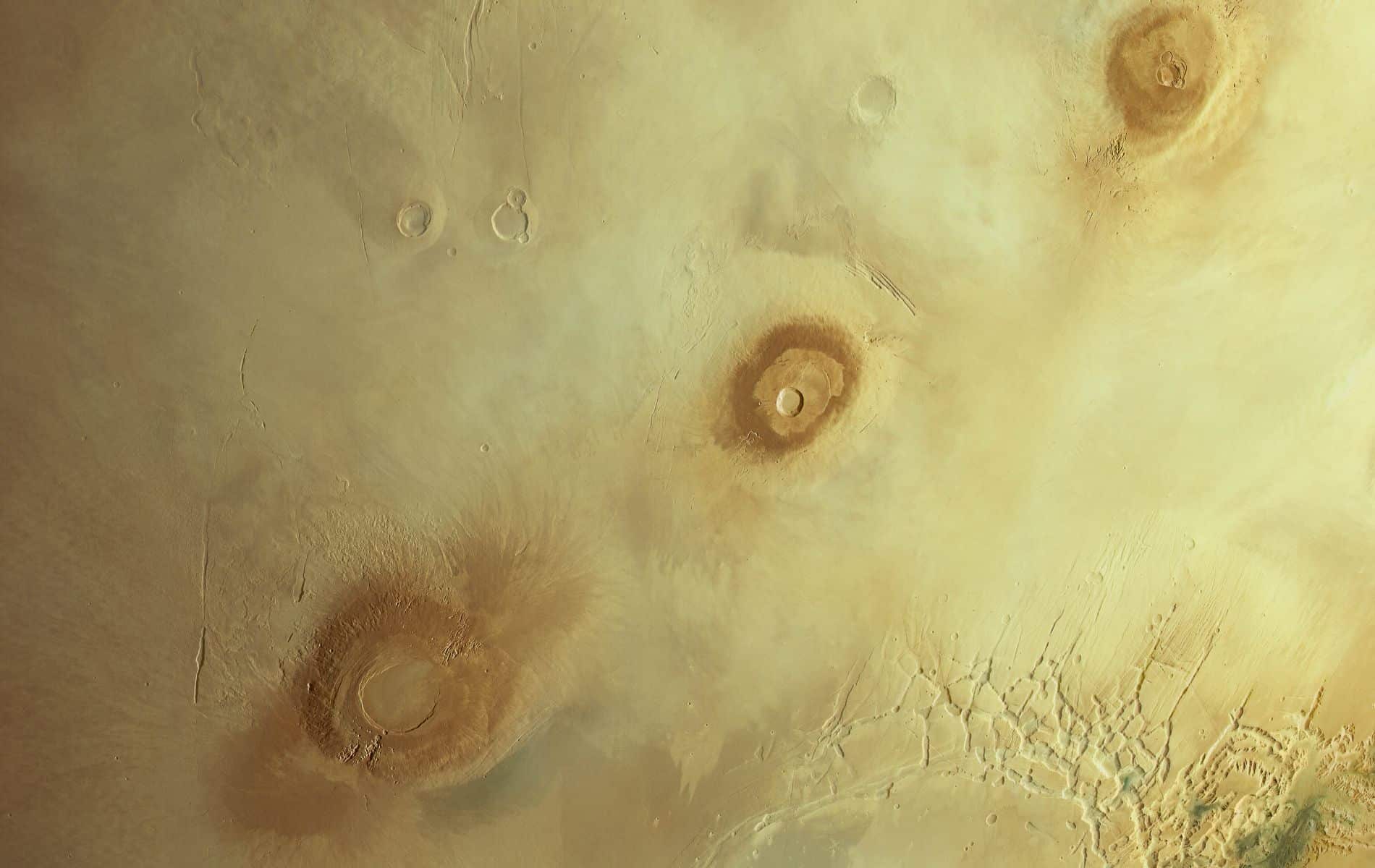
The Mars Express probe arrived at Mars at the end of 2003, and has been orbiting the red planet for nearly 21 years. In that time it has completed 25,000 orbits around Mars. A huge achievement that the probe is celebrating by presenting a stunning image of Mars.
The picture shows a large part of the surface of Mars, and shows some of the most famous volcanoes on the red planet. This is how we see Olympus Mons; Not only is it the largest volcano on Mars, but also the largest in our solar system! The height of the volcano is about 22 kilometers, and its area is 300,000 square kilometers, seven times larger than the area of the Netherlands.
Large volcanoes
However, in addition to Olympus Mons, more volcanoes can be seen in the image. Ascarius mons, for example. With a height of 18 kilometers, it can also be considered among the largest volcanoes on Mars. The volcanoes Arsia Mons – slightly higher than Mount Everest – and Pavonis Mons – about 14 kilometers high – can also be seen in the image.
Valley system
Among this trio of volcanoes we find Noctis Labyrinthus; A gorge system comprising valleys up to 30 km wide and up to 6 km deep. The strait system is approximately 1,190 km long; This is comparable to 3.5 times the distance between Groningen and Maastricht.
clouds
What stands out below are the blue tones in the sandy-toned image. It is caused by clouds. At the bottom there are updrafts (Lee wave clouds) to see. They are caused by air being forced over an obstacle, for example, a mountain.

Phobos
If you look closely, you'll see that Mars wasn't just immortalized by Mars Express; Moon Phobos can also be seen in the image. and diagonally below Arsia Mons. Phobos is very close to Mars; The distance between the two celestial bodies is only 6,000 kilometers. For comparison, our moon orbits the Earth at a distance of about 385,000 km.
A lot of work has been done
to Great picture The European Space Agency (ESA) is celebrating the 25,000th orbit of the Mars Express spacecraft. The space probe completed its 25,000-orbit orbit in October 2023. But only now has the European Space Agency taken a closer look at it. Not just like this, but also looking at what Mars Express taught us about the Red Planet as it orbited Mars. For example, the probe mapped the Martian atmosphere and provided more information about how water on the Red Planet deteriorated over time. The probe also studied the two moons of Mars – Phobos and Deimos – in unprecedented detail and captured these stunning images of Mars.
If it is up to the European Space Agency, the old spacecraft will continue to do this for a while. In 2023, the Mars Express mission will be extended – for the umpteenth time. It was then agreed that the Mars Express vehicle would orbit Mars until at least 2026. The information that the space probe continues to collect is extremely valuable. Not just because we're learning more about Mars. But also because the information could be important for upcoming Mars missions. For example, the European Space Agency hopes to send a rover to Mars sometime in the coming years to search for traces of (decayed) Martian life. NASA wants to pick up materials collected on Mars by the Mars rover Perseverance and bring them to Earth. The more we learn about the Red Planet – for example via Mars orbiters such as Mars Express – the greater the chance that such ambitious missions will succeed.

“Total coffee specialist. Hardcore reader. Incurable music scholar. Web guru. Freelance troublemaker. Problem solver. Travel trailblazer.”






More Stories
GALA lacks a chapter on e-health
Weird beer can taste really good.
Planets contain much more water than previously thought